What is the Difference Between RAM and ROM?
Welcome to our exploration into the digital world’s core components! In the realm of computing, two fundamental elements reign supreme: RAM and ROM. These two acronyms, often tossed around in tech discussions, underpin the functionality of our devices. But what exactly sets RAM and ROM apart? In this blog, we embark on a journey to demystify these essential components in the simplest of terms. So buckle up as we unravel the mysteries behind RAM and ROM, shedding light on their roles, differences, and significance in the digital landscape. Let’s dive in!
Table of Contents
ToggleTable of Contents
Difference Between RAM and ROM?
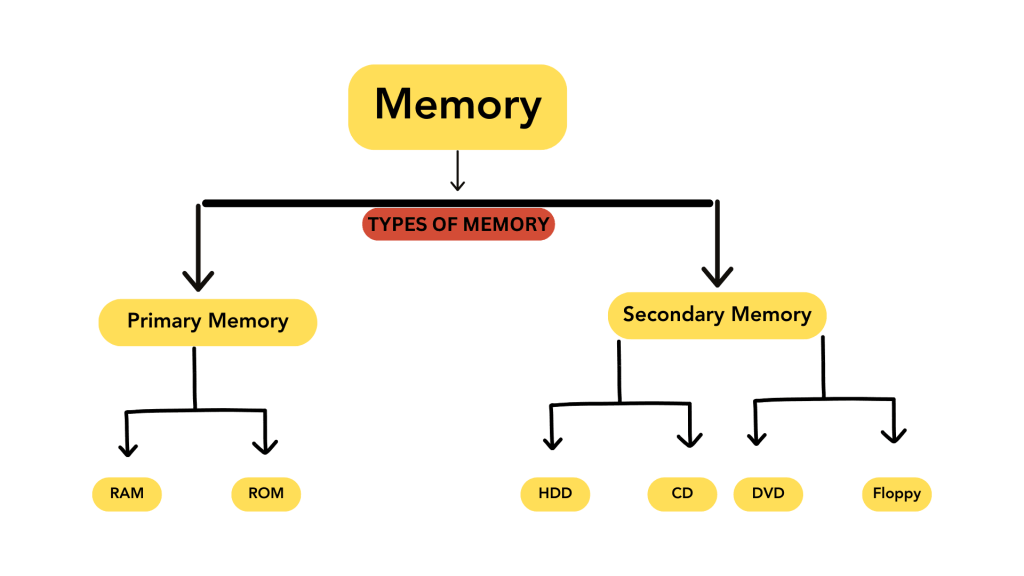
In the world of computers, memory plays a crucial role in storing data and information, either temporarily or permanently. This storage can be divided into two main types:
*Primary Memory
*Secondary Memory
What is Primary Memory?
Primary memory, also known as main memory, refers to the storage space in a computer where data and instructions are accessed and processed directly by the CPU (Central Processing Unit). It is like the computer’s short-term memory, where information is temporarily stored while the computer is running. Primary memory is fast, allowing the CPU to quickly access the data it needs to perform tasks efficiently. Examples of primary memory include Random Access Memory (RAM) and cache memory.
What is Secondary Memory?
Secondary memory refers to a type of storage in computers that holds data and information for the long term. Unlike primary memory, which is fast but temporary, secondary memory retains data even when the computer is turned off. It acts as a permanent storage solution, allowing users to store large amounts of data such as documents, photos, and videos. Common examples of secondary memory include hard disk drives (HDDs), solid-state drives (SSDs), USB flash drives, and memory cards. It serves as a reliable repository for data that users want to access and preserve over time, making it an essential component of computing systems.
Comparison Table for RAM & ROM:
| Feature | RAM (Random Access Memory) | ROM (Read-Only Memory) |
| Type of Memory | Volatile memory (temporary storage). | Non-volatile memory (permanent storage). |
| Function | Stores data actively used by the computer’s CPU. | Contains firmware or software essential for booting up the system and basic functionalities. |
| Read/Write Access | Read and write access during the computer’s operation. | Typically read-only; data is written during manufacturing and remains constant. |
| Data Retention | Loses data when power is turned off or during a restart. | Retains data even when the power is turned off. |
| Usage in Devices | Used in active processes like running applications, open files, etc. | Found in devices to store essential system instructions and cannot be modified by regular users. |
| Modifiability | Can be modified and updated with new data during the computer’s operation. | Generally not user-modifiable; contents are fixed during manufacturing. |
| Speed | Faster access times for reading and writing data. | Typically slower access times compared to RAM. |
| Examples | DDR4, DDR3, etc. in computers and smartphones. | BIOS/UEFI firmware, firmware in embedded systems. |
Difference between Ram and Rom in Laptop & Computers
Diving into the intricate workings of laptops and computers, we encounter two fundamental components: RAM and ROM. These elements, though distinct in nature, collaborate to drive the functionality of our devices. RAM, or Random Access Memory, serves as the dynamic workspace where active data is swiftly processed, akin to a bustling desk space. Meanwhile, ROM, or Read-Only Memory, stores essential system data permanently, acting as a secure vault of instructions and firmware. Join us as we unravel the differences between RAM and ROM, exploring their roles in powering our digital experiences. Let’s embark on a journey through the heart of memory in computing!
RAM in Laptop & Computers:
| Memory Type | Characteristics | Year Established |
| RAM | Volatile, temporary storage for active data in computers. | 1960 |
| DDR1 | Older technology, limited capacity and speed in computers. | 2000 |
| DDR2 | Improved capacity and speed compared to DDR1 in computers. | 2003 |
| DDR3 | Further enhancement in capacity and speed in computers. | 2007 |
| DDR4 | Latest technology, higher speeds and capacities in computers. | 2014 |
ROM in Laptop & Computers:
| Memory Type | Characteristics | Year Established |
| ROM | Non-volatile, stores essential system data in computers. | 1956 |
| SSD (SATA) | Fast read and write speeds, enhances performance in computers. | 2008 |
| SSD (M.2) | Compact form factor, designed for ultrabooks and thin laptops. | 2013 |
| SSD (NVMe) | High-speed data transfer, suitable for performance in computers. | 2015 |
| HDD | Traditional, slower compared to SSD, for large storage. | 1956 |
Difference between Ram and Rom in Digital Electronics
In digital electronics, RAM (Random Access Memory) and ROM (Read-Only Memory) serve distinct purposes: RAM provides volatile, temporary storage for active data, while ROM stores non-volatile, essential system data. Here’s a concise comparison:
| RAM | ROM |
| Volatile; data is lost when powered off | Non-volatile; retains data even when powered off |
| Used for temporary storage of active data | Stores essential system instructions and data |
| Allows for quick read and write operations | Read-only access; data cannot be modified |
| Enables dynamic allocation of memory resources | Provides firmware and boot-up instructions |
In digital electronics, RAM and ROM offer complementary functions, ensuring smooth operation and storing critical system information.
In conclusion, understanding the differences between RAM and ROM is essential for grasping their roles in digital electronics. While RAM facilitates swift data processing and temporary storage, ROM holds vital system instructions and data persistently. Whether you’re looking to enhance your device’s performance with RAM upgrades or ensure seamless system operations with ROM installations, choosing the right services is paramount. For reliable and efficient installation or upgrades of RAM and ROM in your laptops and computers, reach out to AMIT Services. With their expertise and commitment to quality service, you can optimize your devices for enhanced productivity and performance. Don’t hesitate to take action and upgrade your digital experience today with AMIT Services!


![[EXPERT ADVICE] Fixing Monitor No Signal Issues within minutes](https://www.amitservices.in/wp-content/uploads/2024/02/Your-paragraph-text-1-768x432.png)


